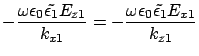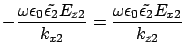: Excitation of surface plasmon
: Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR)
: Metal Surface
The electron charges on metal boundary can perform coherent fluctuations
which are called surface plasma oscillations. The fluctuations are confined
at the boundary and vanishes both inside and outside of the metal surface.
This plasmon waves have  -character because the surface charge induce the
discontinuity of the electric field in the surface normal
-character because the surface charge induce the
discontinuity of the electric field in the surface normal  -direction, but
-direction, but
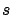 -waves has only
-waves has only 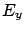 component (no
component (no 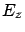 component).
component).
Now we consider the air(medium 2) metal(medium 1) surface where the electric fields
are dumped both side of the interface.
metal(medium 1) surface where the electric fields
are dumped both side of the interface.
For medium 2(air) 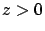 and pure imaginary
and pure imaginary 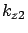
For medium 1(metal) 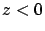 and pure imaginary
and pure imaginary 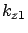
From the Condition I, we get
From condition IV,
From condition III,
For surface plasmon mode
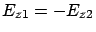 , then
the surface plasmon can be observed when
, then
the surface plasmon can be observed when
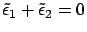 .
.
From Eq.4 and
From the  component,
component,
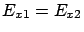 then
then
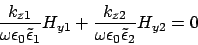 |
(173) |
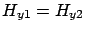 then
then
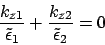 |
(174) |
From eq.(23)
From the last two equations
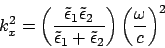 |
(178) |
If we remind that
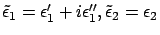
If we assume
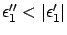
The surface plasmon decay in 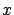 -direction can be evaluated from
-direction can be evaluated from 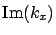 because the intensity decreased as
because the intensity decreased as
![$\exp [-2 {\rm Im}(k_x) x]$](img412.png) .
The decay length
.
The decay length 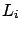 may be
may be
![\begin{displaymath}
L_i = [ 2 {\rm Im}(k_x)]^{-1} = \frac{c}{\omega} \left( \fra...
...epsilon_2 } \right)^{-3/2}\frac{\epsilon^{'2}_1}{\epsilon''_1}
\end{displaymath}](img414.png) |
(184) |
For the water|gold interface the decay lengths 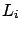 are
6.4
are
6.4 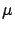 m for gold (16.6
m for gold (16.6 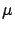 m for air|gold surface),
12.3
m for air|gold surface),
12.3 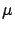 m for silver, and 5.5
m for silver, and 5.5 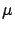 m for aluminum.
There are also temporal decay, please refer the Raether's book for detail.
m for aluminum.
There are also temporal decay, please refer the Raether's book for detail.
The dispersion relation become close to the light line
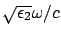 at small
at small 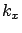 , and at large
, and at large 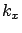
If we use Eqs. (186) and (190) we can get the dispersion relation as shown in the
Figure below.
�$B?^�(B 9:
Surface plasmon dispersion on gold surface. The energy of bulk plasmon is
3.22 eV, and surface plasmon is 2.28 eV.
|
|
The surface plasmon decay in the 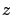 -direction as
-direction as
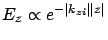 . If we assume
. If we assume
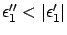 again,
again,
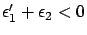 then
then 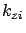 is purely imaginary.
For He-Ne laser (632.8 nm) on the gold surface
is purely imaginary.
For He-Ne laser (632.8 nm) on the gold surface
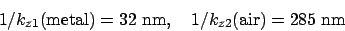 |
(190) |
From the 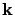 component of
component of
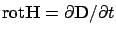
From the 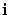 component
component



: Excitation of surface plasmon
: Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR)
: Metal Surface
Yamamoto Masahiro
�$BJ?@.�(B14�$BG/�(B8�$B7n�(B30�$BF|�(B
![]() -character because the surface charge induce the
discontinuity of the electric field in the surface normal
-character because the surface charge induce the
discontinuity of the electric field in the surface normal ![]() -direction, but
-direction, but
![]() -waves has only
-waves has only ![]() component (no
component (no ![]() component).
component).
![]() metal(medium 1) surface where the electric fields
are dumped both side of the interface.
metal(medium 1) surface where the electric fields
are dumped both side of the interface.
![]() and pure imaginary
and pure imaginary ![]()
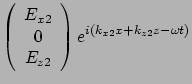
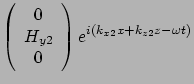
![]() and pure imaginary
and pure imaginary ![]()
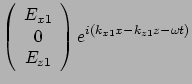
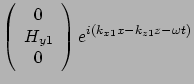
![]()
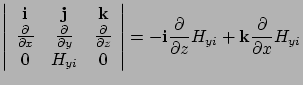
![]() component,
component,
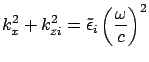
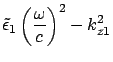
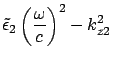
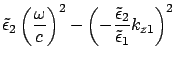
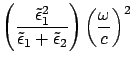
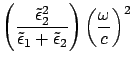
![]()
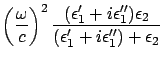
![$\displaystyle \left( \frac{\omega}{c} \right)^2 \epsilon_2
\frac{\epsilon'_1 (\...
...lon'_1\not\!\epsilon''_1 ]}
{(\epsilon'_1 + \epsilon_2 )^2 + \epsilon^{''2}_1 }$](img405.png)
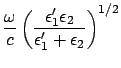
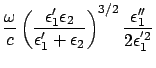
![]() -direction can be evaluated from
-direction can be evaluated from ![]() because the intensity decreased as
because the intensity decreased as
![]() .
The decay length
.
The decay length ![]() may be
may be
![\begin{displaymath}
L_i = [ 2 {\rm Im}(k_x)]^{-1} = \frac{c}{\omega} \left( \fra...
...epsilon_2 } \right)^{-3/2}\frac{\epsilon^{'2}_1}{\epsilon''_1}
\end{displaymath}](img414.png)
![]() at small
at small ![]() , and at large
, and at large ![]()
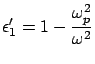
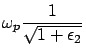
![\includegraphics[width=8cm]{goldsurfplasmondisp.eps}](img422.png)
![]() -direction as
-direction as
![]() . If we assume
. If we assume
![]() again,
again,
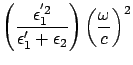
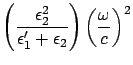
![]() component of
component of
![]()